Enhance Your English Fluency with Essential Medical Vocabulary
Table of Content
Introduction
Have you ever had an encounter that made you wish you understood medical English a little better? Picture this: An ESL student, fresh off the plane, confounded by a sudden sharp headache, tries to explain his ailment to a pharmacist, but mistakenly uses the word hammer instead of headache. He left with a bemused smile from the pharmacist and a construction tool recommendation rather than the needed medicine.
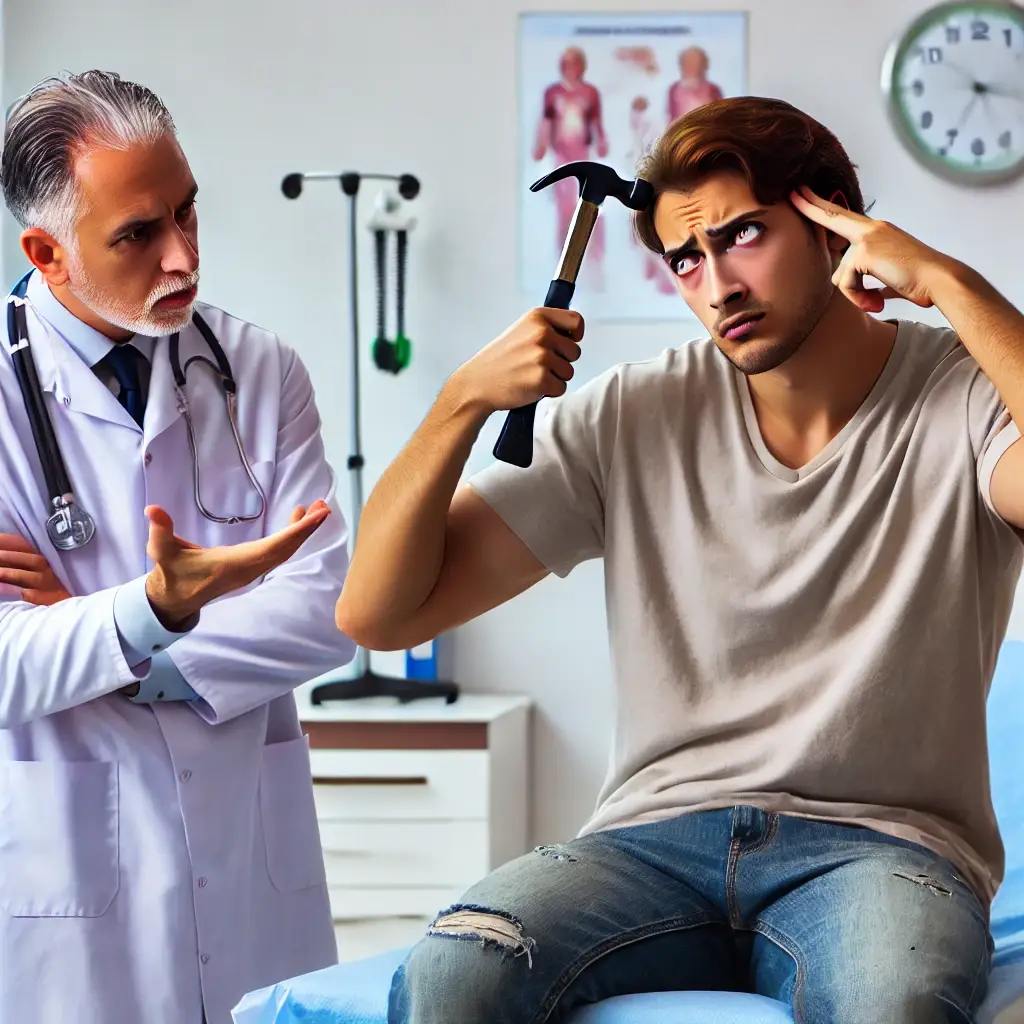

Instances like this underscore why understanding medical vocabulary is crucial, especially for those trying to master English as a second language (ESL). Navigating healthcare can be a labyrinthine task, even for native speakers. Grappling with medical terminologies can seem daunting when you are healthy, let alone in the event of an illness or emergency. If you are striving for fluency, then familiarizing yourself with essential medical English words becomes imperative.
Excelling in your work or school health classes, conversing readily with healthcare professionals, and being equipped to handle unforeseen health-related situations all hinge on a robust understanding of the medical lexicon. This blog post aims to serve as a guide, offering support to ESL students to aid them in decoding the top 50 most essential medical words. By learning and integrating these into your daily verbal exchanges, you can mitigate confusion and ensure you aptly understand varying environments and situations.
Read on to find a list that includes basic anatomy and body parts, health conditions and symptoms, medical procedures and tests, healthcare professionals and places, and medical advice and prevention. This comprehensive guide will broaden your vocabulary and build your confidence when it comes to health-related matters.
Basic Anatomy and Body Parts
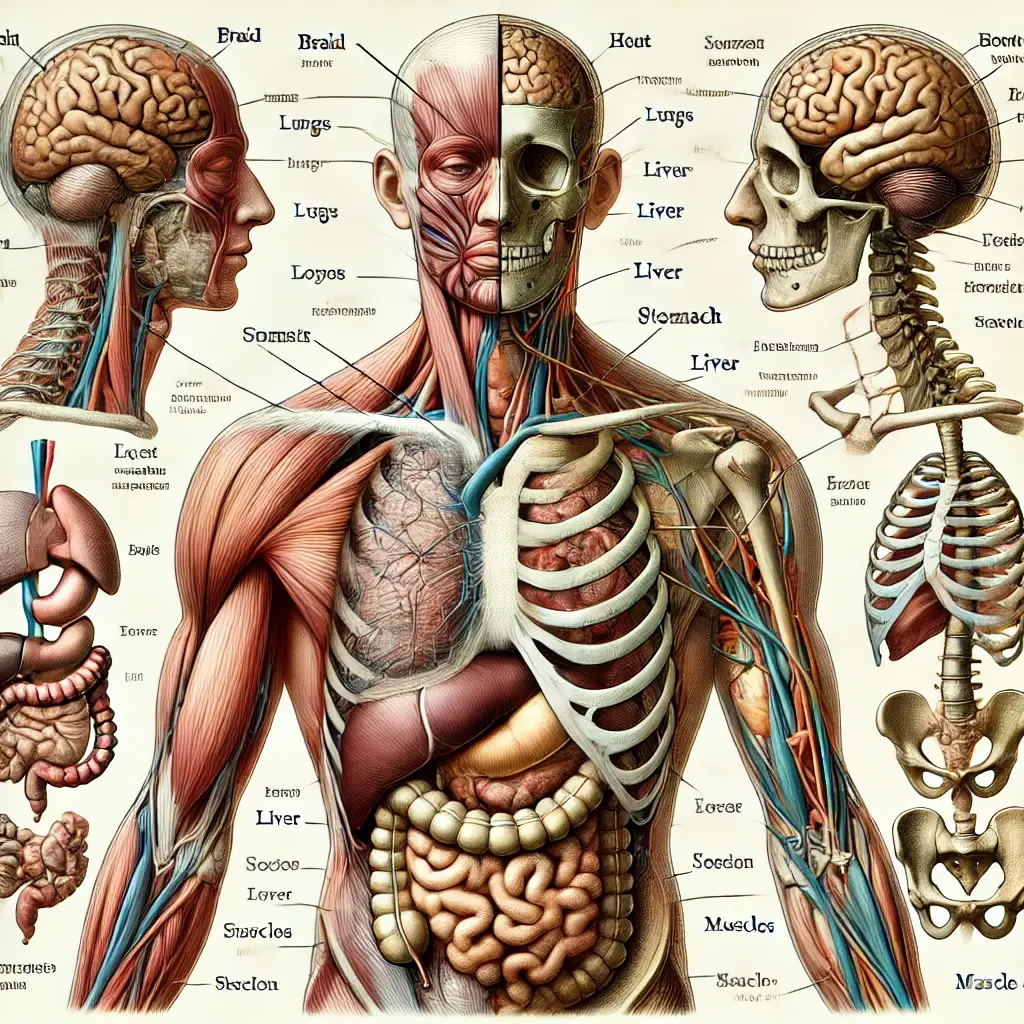
A basic understanding of anatomical terms can be the bridge that links you to healthcare professionals and their advice. Let’s delve into these essential terms:
- Head
- Head, Brain, Eye, Ear, Nose, Mouth
Understanding words related to the head is pivotal due to the head’s significance: it contains our brain, the powerhouse of the body. The brain is responsible for all our movements, thoughts, feelings, and interactions. The eyes, ears, nose, and mouth provide our senses – our interfaces with the world – making it vital to know these words.
- Head, Brain, Eye, Ear, Nose, Mouth
- Limbs
- Arm, Hand, Finger, Leg, Foot, Toe
Our limbs carry out countless daily tasks, ranging from mundane activities like walking to writing essays or playing instruments. Recognizing these words can help accurately describe any injury, pain, or abnormality.
- Arm, Hand, Finger, Leg, Foot, Toe
- Organs
- Heart, Lung, Liver, Stomach, Intestine, Kidney
Your organs work together seamlessly to keep you alive and functioning. It is their interdependence that prompts knowledge of these terms to be essential – issues in one organ can easily affect another.
- Heart, Lung, Liver, Stomach, Intestine, Kidney
- Bones and Muscles
- Bone, Joint, Muscle, Neck, Back, Knee
Our bones provide a frame, our muscles the power for movement, and joints facilitate flexibility. Any discomfort or condition implicating these parts is best described using these particular words.
- Bone, Joint, Muscle, Neck, Back, Knee
- Skin
- Skin, Hair
As our body’s largest organ and the first line of defense against external pathogens, understanding words related to skin is paramount. This can aid in accurately describing symptoms like rashes, spots, or other conditions.
- Skin, Hair
Health Conditions and Symptoms
When it comes to your health, being able to describe what you feeling accurately can significantly affect whatever care you receive.
- Pain
- Headache, Stomachache, Hurt, Injury, Sore
Pain is your body’s way of signaling that something is wrong. Knowing how to express different types of pain can aid healthcare providers in diagnosing and treating you more effectively.
- Headache, Stomachache, Hurt, Injury, Sore
- Illnesses
- Flu, Cold, Fever, Infection, Disease, Sickness, Virus
Infections and diseases can wreak havoc on your health. Knowledge of terms related to illnesses can aid in your communication with healthcare providers and allow you to understand your condition better.
- Flu, Cold, Fever, Infection, Disease, Sickness, Virus
- Issues
- Bleeding, Broken bone, Burn, Rash, Lump, Swelling
Often discomfort or injuries are reflected through symptoms like bleeding or swelling. Learning these terms can help you communicate your condition more efficiently and relieve discomfort faster.
- Bleeding, Broken bone, Burn, Rash, Lump, Swelling
- Emotions
- Sad, Anxious, Stressed, Nervous, Depressed
Physical health and mental health are intertwined. Conveying your emotional state is as crucial as explaining your physical symptoms, as they may be a symptom or cause of other health issues.
- Sad, Anxious, Stressed, Nervous, Depressed
- Sensations
- Itch, Ache, Dizzy, Nauseous, Numb
Sometimes you might not be in pain or suffering from a particular disease – you might just feel off. Terms that describe sensations can assist you in articulating what you cannot categorize as illness or pain.
- Itch, Ache, Dizzy, Nauseous, Numb
Learning proper medical terms and integrating them into your vocabulary can indeed serve as a beneficial, lifelong learning tool. Onward to the next step of your educational journey!
Mental Health (H2)
Introduction (H3)
Mental health is just as important as physical health, especially when you’re away from home. These terms can help you discuss mental health issues with healthcare providers.

Terms (H3)
- Anxiety: A feeling of worry or fear.
- Example: I experience anxiety when flying.
- Depression: A mood disorder causing persistent feelings of sadness.
- Example: She was diagnosed with depression last year.
- Therapy: Treatment intended to relieve or heal a disorder.
- Example: He’s been going to therapy to improve his mental health.
Women’s Health
Introduction
Women’s health encompasses a range of topics specific to women. These terms can be useful during visits to a gynecologist or general healthcare provider.

Terms (H3)
- Menstruation: The monthly shedding of the uterine lining.
- Example: My menstruation cycle is usually 28 days.
- Pregnancy: The condition of carrying a developing fetus.
- Example: She confirmed her pregnancy with a test.
- Contraception: Methods used to prevent pregnancy.
- Example: They discussed different forms of contraception during the appointment.
Men’s Health
Introduction
Men also have health concerns specific to them. These terms can be useful during visits to a urologist or general healthcare provider.

Terms
- Prostate: A gland in men that produces fluid for semen.
- Example: He went for a prostate exam.
- Testosterone: The primary male sex hormone.
- Example: Low testosterone can affect mood and energy.
- Erectile Dysfunction: The inability to maintain an erection.
- Example: He sought treatment for erectile dysfunction.
Pediatrics
Introduction
If you’re traveling with children, knowing pediatric terms can be incredibly helpful in case of illness or injury.

Terms
- Vaccination: Treatment with a vaccine to produce immunity.
- Example: The child received a vaccination for measles.
- Pediatrician: A doctor specializing in children’s health.
- Example: We took our son to the pediatrician for a check-up.
- Colic: Severe pain in the abdomen or bowels.
- Example: The baby was crying due to colic.
Elderly Care
Introduction

Elderly individuals have unique healthcare needs. These terms can be useful when interacting with healthcare providers specializing in geriatric medicine.
Terms
- Arthritis: Inflammation of one or more joints.
- Example: My grandmother suffers from arthritis.
- Dementia: A decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life.
- Example: His grandfather was diagnosed with dementia.
- Osteoporosis: A condition where bones become weak and brittle.
- Example: She is taking medication for osteoporosis.
This guide aims to equip you with essential medical terms that can be beneficial during your travels. Remember, it’s always best to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate information and diagnosis.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.
Adapting to the Healthcare System in English-Speaking Countries
1. Patient Rights and Responsibilities
Understanding your rights as a patient in a foreign country can often be overwhelming. Hence, it is important to master these words:
- Consent: This is the agreement you provide for a treatment or procedure. All patients have the right to informed consent which means knowing about the benefits, risks, and alternatives of a procedure.
- Privacy: This relates to the confidentiality of your health information. You have the right to control who accesses your medical records.
- Respect: This term refers to the dignity and compassion with which medical providers should treat you.
- Responsibility: This means understanding and following through with your obligations as a patient, such as following medical advice, attending appointments, and making payments.
2. Insurance Terms and Billing
Navigating the health insurance system can be complicated, but it is simpler with the right vocabulary:
- Premium: This is the amount you pay for your health insurance every month.
- Deductible: This is the amount you must pay out of pocket before the health insurance begins to cover your costs.
- Co-payment (Co-pay): This is a fixed amount you have to pay for a covered service after you pay your deductible.
- Out-of-pocket maximum: This is the most you have to pay for covered services in a policy period. After you reach this limit, your insurance will cover 100% of the costs.
3. Appointment and Registration
Scheduling appointments and going through hospital registration can be smooth with these terms:
- Appointment: A previously arranged meeting with a healthcare provider.
- Walk-in: A service where you can visit a healthcare provider without a prior appointment.
- Referral: A recommendation to see another healthcare provider or specialist for further examination or treatment.
- Register: Process of getting yourself into the hospital system by providing necessary details like name, address, insurance information, etc.
- Emergency: A condition needing immediate medical attention.
Conclusion: The Importance of Medical Vocabulary for ESL Students
Mastering the 50 medical terms and phrases that we discussed is vital for any ESL student entering an English-speaking healthcare environment. It allows you to confidently communicate about your body, conditions, and procedures and engage with the healthcare system.
Not only do these words help describe a health condition, but they also aid in understanding prescriptions, advice from health professionals, and navigating through the medical system. Whether you are visiting the doctor, speaking to your health provider over the phone, or watching a medical drama, these words will surely come in handy.
It is crucial to not only understand these terms but also be able to recall and use them in appropriate contexts. Remember, healthcare professionals are there not only to treat but also to guide and clarify any doubts you might have. Don’t hesitate to ask questions or clarify if you don’t understand a term.
The journey of learning might seem vast, but one step at a time gets you there. Use this guide as a building block for your medical vocabulary mastery. Download our medical vocabulary cheat sheet and start expanding your knowledge today. Be curious, keep learning, and continue practicing. After all, your health, and effective communication about it, are crucial.
Ready to take on your medical English journey? Start off with mastering these 50 must-know medical words!

